Indonesia, a vast archipelago nation with unique geographical challenges, is aggressively building its digital future. To bridge these significant barriers and ensure widespread connectivity, the nation has deployed monumental projects: the Palapa Ring fiber optic network and advanced satellite technology. These initiatives are forming a crucial digital backbone, rapidly transforming access to high-speed internet and digital services across its thousands of islands.
The impact of this digital transformation extends beyond mere access, fostering inclusive growth and unlocking new opportunities for millions. From education to healthcare, these core connectivity projects underscore Indonesia’s commitment to innovation and its unique approach to redefining tech through local solutions.
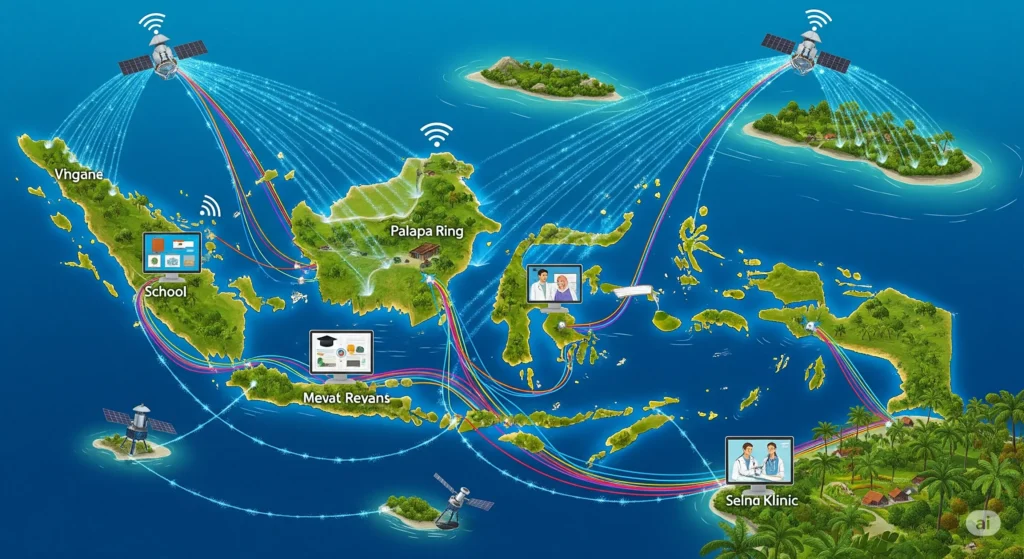
For a deeper understanding of Indonesia’s broader innovation landscape and unique solutions, explore our comprehensive pillar article: Innovation in Indonesia: How Unique Solutions Drive Change.
See Table of Contents
Palapa Ring: Building the Fiber Optic Artery of the Archipelago
The Palapa Ring project stands as a monumental effort in Indonesia’s digital transformation. This ambitious nationwide fiber optic network was conceived to connect every regency and city across the vast archipelago, laying the groundwork for equitable access to high-speed internet and fostering a more unified digital society.
Palapa Ring’s Technical Blueprint: Bridging the Digital Divide
The Palapa Ring is arguably Indonesia’s most ambitious national infrastructure project aimed at achieving digital equity. Conceived to complement existing networks, it establishes a robust, high-speed fiber optic backbone spanning over 36,000 kilometers, connecting 514 cities and regencies across the archipelago. This strategic initiative was designed to ensure that even remote and underdeveloped regions gain access to reliable internet, thereby eradicating the digital divide that historically plagued such diverse geography.
Divided into three distinct packages—West, Central, and East—the project overcame immense logistical challenges, traversing dense jungles, mountainous terrains, and vast underwater expanses. The Western package linked Sumatra, Java, and Kalimantan; the Central package connected Kalimantan, Sulawesi, and North Maluku; while the Eastern package extended connectivity to Papua, Maluku, and Nusa Tenggara.
Completed in 2019, the network’s deployment required significant investment and engineering prowess, marking a pivotal moment in Indonesia’s digital readiness. (A study by Eschachasthi, Purwa, & Cendekia, 2022, found a positive and significant impact of PRP infrastructure on connectivity, though not necessarily on direct economic activity, available via DOI: 10.34123/icdsos.v2021i1.99.)
The implications of the Palapa Ring network are profound, extending far beyond mere internet access. By providing a uniform, high-capacity infrastructure, it facilitates the expansion of e-commerce, remote education, telemedicine, and government services to previously underserved areas. This foundational layer of connectivity is crucial for stimulating local economies, fostering entrepreneurship, and integrating disparate regions into the national and global digital economy, thereby ensuring no island is left behind in the era of rapid technological advancement.
Video Insight: Understanding the Palapa Ring Project
Here is a link to a video that provides further understanding of the Palapa Ring project:
The video above provides an understanding that the Palapa Ring Project is an effort to develop a telecommunications network across all regencies and cities using Submarine Cable Communication Systems (SKKL) and Fiber Optic Communication Systems (SKSO). This video highlights the noble aspirations of this project to realize national sovereignty and resilience in ICT, positioning Indonesia as a regional and international telecommunications hub, and promoting equitable development and a healthy competitive climate in the telecommunications sector.
Palapa Ring: Foundational Impact on Connectivity
In essence, the Palapa Ring project is more than just a massive infrastructure undertaking; it is a foundational pillar for Indonesia’s digital future. By systematically connecting the archipelago with a high-capacity fiber optic backbone, it has laid the essential groundwork for widespread internet access, fostering economic growth, and enhancing public services across all regions. This ambitious endeavor exemplifies Indonesia’s commitment to inclusive development, ensuring that its geographical diversity does not hinder digital equality.
Palapa Ring Implementation: Navigating Archipelago Complexities
Implementing a nationwide fiber optic network across an archipelago as vast and geographically diverse as Indonesia presented unprecedented challenges. Beyond the sheer scale, the project had to contend with complex undersea topographies, active seismic zones, dense jungle terrains, and the need to connect remote, sparsely populated islands. This required innovative engineering solutions and meticulous planning to ensure the network’s resilience and reach.
The deployment involved laying thousands of kilometers of submarine cables through deep oceans, navigating volatile currents and protecting against potential damage from fishing activities or natural disasters. On land, the process required extensive clearing, trenching, and the construction of numerous tower sites in areas lacking existing infrastructure. Moreover, securing land rights and managing community engagement across diverse local cultures added layers of socio-political complexity to the technical hurdles.
These multifaceted challenges often led to delays and increased costs, demanding continuous adaptation and strategic partnerships throughout the project’s phases. (For detailed insights into national fiber optic backbone strategies in rural areas of Indonesia, see Asvial, 2019, available via DOI: 10.1109/ICIRD47319.2019.9074750.)
Despite these formidable obstacles, the successful completion of the Palapa Ring underscores Indonesia’s determination to overcome geographical fragmentation through digital means. The experience gained from this project provides invaluable lessons for future infrastructure development in challenging environments globally. It demonstrated the critical role of robust project management, inter-agency cooperation, and public-private partnerships in translating an ambitious vision into a tangible reality, ultimately impacting millions by extending digital access where it was once deemed impossible.
Video Insight: Overcoming Connectivity Barriers
For a deeper insight into how the Palapa Ring project tackles connectivity issues in Indonesia’s diverse regions, watch this video from CNA:
The video highlights the network’s ambitious goal of bringing high-speed internet to even the country’s poorest and most remote areas, showcasing the significant logistical and geographical hurdles that had to be overcome to achieve this unprecedented level of digital inclusion across the archipelago.
Conclusion: A Triumph of Archipelagic Connectivity
In summary, the successful implementation of the Palapa Ring network represents a monumental triumph over Indonesia’s unique geographical and logistical challenges. It stands as a testament to the nation’s resolve in building a cohesive digital infrastructure. The strategies employed and lessons learned from navigating the complexities of an archipelagic environment provide a valuable blueprint for future large-scale connectivity projects, not only in Indonesia but globally, reinforcing the commitment to inclusive digital access.
Satellites: Reaching Remote and Underserved Communities
Satellite Connectivity: Bridging the Last Mile in Indonesia
While fiber optic networks like Palapa Ring form the high-capacity backbone, satellite technology plays an indispensable role in extending connectivity to Indonesia’s most remote and challenging terrains. For islands and regions where laying physical cables is economically unfeasible or geographically impossible, satellites offer the only viable solution for immediate and widespread internet access. This complementary approach ensures that truly no corner of the archipelago is left digitally isolated.
Indonesia has actively invested in a robust satellite infrastructure to support this ‘last mile’ connectivity. Programs like the SATRIA-1 (Satellite of the Republic of Indonesia-1) project, launched in 2023, exemplify this commitment. As the largest high-throughput satellite (HTS) in Asia, SATRIA-1 is designed to provide internet access to approximately 150,000 public service points, including schools, hospitals, and government offices in remote areas, significantly impacting digital inclusion.
(For a techno-economic analysis of SATRIA-1’s role in government communications, refer to research available via DOI: 10.1109/COMNETSAT63286.2024.10862510.) This initiative leverages advanced satellite communication to overcome topographical barriers, providing direct-to-community internet services where terrestrial infrastructure is absent.
The deployment of satellite internet not only connects isolated communities but fundamentally transforms their access to essential services. It enables remote learning, telehealth consultations, and facilitates financial inclusion by supporting digital transactions, thereby integrating these populations into the national digital economy. Beyond direct services, satellite connectivity fosters social cohesion and provides crucial communication channels during disaster relief, underscoring its vital role as a lifeline for national development and resilience in an archipelagic context.
Video Insight: The Launch of SATRIA-1
Witness the launch of a key component in Indonesia’s satellite connectivity strategy with this short video:
This clip showcases the successful launch of Indonesia’s largest telecommunication satellite by SpaceX, an event pivotal to extending high-speed internet access to the nation’s vast, underserved regions. It visually emphasizes the technological leap Indonesia is taking to ensure digital inclusion reaches every corner of its diverse archipelago, especially where terrestrial infrastructure remains challenging.
Conclusion: Satellites as Critical Enablers of Digital Inclusion
In conclusion, satellite technology stands as an indispensable pillar in Indonesia’s quest for universal digital access. By providing reliable internet connectivity to the most remote and challenging areas, satellites bridge the critical “last mile” gap that fiber optics cannot reach. This strategic investment not only empowers isolated communities with access to vital services but also reinforces Indonesia’s commitment to building a truly connected and resilient digital nation, ensuring equitable development across its vast archipelago.
Diverse Satellite Technologies: Tailoring Solutions for Indonesia’s Unique Needs
Indonesia’s vast and fragmented geography necessitates a multi-faceted approach to satellite connectivity, moving beyond traditional geostationary orbit (GEO) satellites. While GEO satellites, positioned high above the equator, offer wide coverage crucial for a country with thousands of islands, their inherent latency can limit performance for real-time applications. Therefore, Indonesia is increasingly exploring the benefits of other satellite technologies to meet diverse user needs and enhance overall digital experience across its archipelago.
The emergence of Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) and Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite constellations presents new opportunities for Indonesia. LEO satellites, in particular, orbit much closer to Earth, significantly reducing latency and enabling high-speed, low-delay internet crucial for applications like online gaming, video conferencing, and remote surgery in areas otherwise isolated. While government initiatives like SATRIA-1 (a GEO satellite) address mass public service connectivity, private sector players and future government strategies are considering LEO solutions, such as Starlink, to provide more performant internet services, especially for remote businesses or high-demand users, thereby complementing the existing infrastructure and addressing specific market segments.
(For a techno-economic analysis comparing SATRIA-1 and Starlink for government communications in Indonesia, see research available via DOI: 10.1109/COMNETSAT63286.2024.10862510.)
This strategic diversification in satellite technology allows Indonesia to tailor connectivity solutions to distinct geographical and user requirements. By leveraging the strengths of GEO for broad coverage and LEO for low-latency, high-speed access, the nation can optimize its digital infrastructure investment. This holistic approach ensures that digital transformation is not a one-size-fits-all solution but a responsive strategy that addresses the unique ‘last mile’ challenges of each island and community, solidifying Indonesia’s position as a leader in innovative connectivity solutions for complex geographies.
Video Insight: Understanding Satellite Internet in Indonesia
For an accessible look into the practicalities of satellite internet in Indonesia, watch this short video:
Although in Indonesian, the video touches upon fundamental questions surrounding satellite internet, such as its current availability and cost, directly relevant to the Indonesian context. It helps illustrate the consumer perspective and ongoing discussions about how satellite technology is becoming a tangible option for Indonesian users, highlighting its role in expanding connectivity across the archipelago.
Conclusion: Tailored Satellite Solutions for a Connected Indonesia
In conclusion, Indonesia’s strategy to integrate diverse satellite technologies—from traditional GEO to advanced LEO constellations—is a critical response to its unique geographical imperatives. This multi-layered approach ensures that connectivity solutions can be precisely tailored to various needs, overcoming the limitations of any single technology. By embracing this strategic flexibility, Indonesia is not only expanding access but also building a resilient and future-proof digital infrastructure capable of supporting its vast and diverse population.
Transformative Impact: Driving Digital Economy, Education, and Health
Connectivity as a Catalyst: Fueling Indonesia’s Digital Transformation
The expansion of robust digital connectivity, driven by initiatives like Palapa Ring and satellite technology, serves as a powerful catalyst for profound socio-economic transformation across Indonesia. Beyond mere internet access, this pervasive connectivity is fundamentally reshaping how communities live, work, and interact. It creates unprecedented opportunities for growth in the digital economy, revolutionizes access to quality education, and significantly enhances healthcare delivery, particularly in previously underserved and remote areas.
In the digital economy, improved connectivity fosters the growth of e-commerce, digital payments, and ride-hailing services, empowering small and medium enterprises (SMEs) and creating new job opportunities, even in rural settings. For education, the ability to access online learning platforms and digital resources bridges geographical gaps, providing students in remote islands with access to the same educational content as their urban peers, thereby enhancing learning outcomes and reducing educational disparities. Furthermore, in healthcare, connectivity facilitates telemedicine, allowing remote consultations, expert second opinions, and more efficient health data management, significantly improving access to medical care in areas with limited physical infrastructure.
(For an analysis on the impact of digital technology development on Indonesia’s economic growth, see research from the International Journal of Research and Review, 2023).
This multi-sectoral impact underscores connectivity’s role as an enabler of inclusive development. By democratizing access to information, markets, and essential services, digital transformation empowers individuals and communities to participate more fully in the national economy and society. The convergence of robust infrastructure and digital literacy paves the way for a more equitable and prosperous Indonesia, where geographical barriers no longer dictate access to opportunities, fostering innovation and resilience across the archipelago.
Video Insight: Digital Jobs & Skills in Asia-Pacific, Including Indonesia
To understand the evolving landscape of digital jobs and skills shaped by connectivity in Indonesia and the wider Asia-Pacific, watch this insightful video:
Based on a joint report by the Asian Development Bank (ADB) and LinkedIn, the video highlights how digital transformation is impacting the workforce, the demand for digital skills, and the significance of online learning. It offers valuable perspectives on how increased connectivity directly contributes to new economic opportunities and educational advancements, particularly relevant to Indonesia’s burgeoning digital economy.
Conclusion: Connectivity’s Transformative Power in Indonesia
In conclusion, Indonesia’s commitment to widespread digital connectivity is proving to be a potent catalyst for national transformation. By fueling the digital economy and revolutionizing access to education and healthcare, connectivity empowers individuals and communities, fostering inclusive growth and bridging development gaps across the archipelago. This strategic investment is not merely about access; it’s about unlocking immense human potential and building a more equitable, resilient, and prosperous digital future for all Indonesians.
Digital Learning in the Archipelago: Transforming Education through Connectivity
Digital learning has emerged as a powerful equalizer in Indonesia’s education landscape, especially with the expansion of internet connectivity. In an archipelago characterized by geographical dispersion, traditional schooling often faces limitations in terms of resource access, qualified teachers, and infrastructure. Connectivity bridges these gaps, allowing students and educators in even the most remote islands to access a wealth of online educational resources, participate in virtual classrooms, and engage in collaborative learning experiences that were previously unimaginable.
The proliferation of digital learning platforms, government initiatives for remote education, and the increasing availability of affordable devices have significantly boosted educational opportunities across Indonesia. For instance, students in isolated regions can now access diverse curricula, participate in national examinations with greater equity, and gain skills vital for the digital age. Teachers benefit from online professional development, access to updated pedagogical materials, and networking opportunities, enhancing teaching quality nationwide.
This digital transformation in education directly addresses disparities and works towards achieving more equitable learning outcomes. (For a systematic review on the effectiveness of online learning platforms in increasing educational access in remote areas, see research published in the Proceeding of International Seminar On Student Research In Education, Science, and Technology, 2024).
The long-term implications of robust digital learning infrastructure for Indonesia are profound. It cultivates a digitally literate generation, better equipped for the demands of the modern workforce and global economy. Furthermore, it fosters continuous learning beyond traditional schooling, enabling lifelong skill development and adaptability.
By integrating connectivity into the core of its educational strategy, Indonesia is not only improving academic performance but also building a more skilled, competitive, and inclusive human capital base essential for sustainable national development.
Video Insight: Shifting Landscape of Digital Jobs & Skills in Asia-Pacific, Including Indonesia
To understand the evolving landscape of digital jobs and skills and their relevance to education in the Asia-Pacific region, including Indonesia, watch this informative video:
Based on a joint report by the Asian Development Bank (ADB) and LinkedIn, this video highlights how digital transformation is influencing the workforce and emphasizing the demand for digital skills. It offers valuable perspectives on how increased connectivity directly contributes to new economic opportunities and educational advancements, which is highly relevant as Indonesia transforms its education system to meet the demands of the digital era.
Conclusion: Connectivity’s Transformative Power in Indonesian Education
In summary, digital learning, empowered by expanding connectivity, is fundamentally transforming Indonesia’s educational landscape. By breaking down geographical barriers and democratizing access to quality resources, it ensures that students across the archipelago, especially in remote areas, receive equitable learning opportunities. This strategic integration of technology into education is pivotal for nurturing a skilled and adaptive workforce and building a more inclusive and prosperous future for Indonesia.
Telemedicine in the Archipelago: Enhancing Health Access through Digital Connectivity
In a vast archipelagic nation like Indonesia, ensuring equitable access to quality healthcare is a monumental challenge, especially for communities living in remote islands and underserved regions. The uneven distribution of medical professionals and healthcare facilities often means residents must travel great distances for basic consultations or specialized care. Here, digital connectivity emerges as a vital lifeline, enabling the widespread adoption of telemedicine to bridge these geographical and logistical gaps and bring essential medical services closer to the people.
Telemedicine platforms, empowered by enhanced internet access, allow patients in remote areas to consult with doctors via video calls, receive diagnoses, and obtain prescriptions without leaving their villages. This significantly reduces travel costs and time, and provides timely access to care, which can be critical in emergency situations. Government initiatives and private health tech companies are actively expanding these services, connecting local community health centers (Puskesmas) with specialists in urban hospitals.
This not only democratizes healthcare access but also supports continuous medical education for rural practitioners. (For a deeper understanding of teleconsultation readiness and disparities in Indonesian healthcare facilities, refer to research published in Frontiers in Public Health, 2024).
The long-term impact of telemedicine facilitated by robust connectivity is transformative for Indonesia’s public health system. It leads to earlier diagnoses, better management of chronic diseases, and improved public health outcomes by enabling widespread health education and preventive care. Moreover, by reducing the burden on central healthcare facilities, it allows for a more efficient allocation of resources. This digital leap in healthcare underscores how strategic investment in connectivity can directly improve the well-being and quality of life for millions of Indonesians, fostering a healthier and more resilient nation.
Video Insight: Telemedicine in Remote Indonesian Health Centers
To see a direct example of telemedicine implementation in Indonesia’s most remote areas, watch this video:
Titled ‘Implementation of Telemedicine and ILP in Puskesmas and Auxiliary Health Centers in Remote and Very Remote Areas’ (original title in Indonesian), this video provides a valuable insight into how digital solutions are being deployed at the grassroots level. It highlights efforts to bring essential health services to isolated communities, demonstrating the practical application of connectivity in overcoming geographical barriers to healthcare access across the Indonesian archipelago.
Conclusion: Connectivity’s Vital Role in Indonesian Healthcare
In conclusion, telemedicine, powered by expanding digital connectivity, is revolutionizing healthcare access across the Indonesian archipelago. By enabling remote consultations and efficient health management, it effectively bridges the vast geographical distances that traditionally hindered medical care for underserved communities. This strategic embrace of digital health solutions is pivotal in building a more equitable, resilient, and accessible healthcare system, ultimately enhancing the well-being and quality of life for all Indonesians, regardless of their location.
Challenges and Future Prospects: Sustaining Indonesia’s Connectivity Growth
Addressing the Digital Divide: Overcoming Connectivity Challenges in Indonesia
Despite significant strides in expanding connectivity, Indonesia still faces substantial hurdles in achieving truly equitable and pervasive digital access. The persistent ‘digital divide’ remains a primary concern, manifesting as disparities in internet availability, quality, and affordability between urban and rural areas, as well as across different socio-economic groups. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for ensuring that the benefits of digital transformation reach all citizens, fostering inclusive growth and preventing further marginalization.
Key challenges include the immense geographical complexities of an archipelagic nation, making last-mile infrastructure deployment incredibly costly and complex. Furthermore, issues of affordability often limit access for lower-income segments, even where infrastructure exists. Beyond physical access, disparities in digital literacy and skills hinder effective internet utilization, especially in remote communities.
Maintaining and upgrading existing infrastructure, alongside ensuring a robust and fair regulatory environment that encourages investment while protecting consumers, are also critical ongoing challenges. (Academic research on the impact of digital divide on Indonesian public services highlights concerns such as low digital literacy and inequality in access; see Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan Pendidikan Indonesia, 2024).
Addressing these multifaceted challenges requires a sustained, multi-stakeholder approach involving government policy, private sector investment, and community empowerment initiatives. Strategies must include innovative financing models, targeted subsidies for underserved areas, and comprehensive digital literacy programs. Successfully bridging the digital divide is not merely an infrastructure project; it is a fundamental prerequisite for sustained national development, social cohesion, and Indonesia’s aspiration to become a leading digital economy, ensuring no citizen is left behind in the digital era.
Video Insight: Navigating Indonesia’s Digital Divide
To gain a deeper understanding of the digital divide in Indonesia, watch this insightful video titled ‘Closing the Gap: Digital Divide in Indonesia’ from UNDP Indonesia:
This video explores the challenges of ensuring equitable digital access across the nation, particularly focusing on geographical and gender disparities in the economic sector. It highlights crucial discussions on how to narrow the digital gap and ensure that the benefits of Indonesia’s accelerating digital transformation are inclusive for all citizens.
Conclusion: Bridging the Divide for an Inclusive Digital Future
In conclusion, while Indonesia has made remarkable progress in expanding digital connectivity, significant challenges remain in fully bridging the digital divide. Overcoming geographical barriers, ensuring affordability, and enhancing digital literacy are paramount to achieving universal and equitable access. A collaborative and strategic approach is essential to transform these challenges into opportunities, ensuring that Indonesia’s digital growth is inclusive and benefits all its citizens, paving the way for a truly connected and prosperous future.
Paving the Way Forward: Indonesia’s Vision for Universal Digital Access
Looking ahead, Indonesia’s commitment to achieving universal digital access and becoming a leading digital economy remains steadfast, despite existing challenges. The vision for future connectivity is multifaceted, focusing not only on expanding infrastructure but also on enhancing the quality and inclusivity of digital services. This forward-looking approach encompasses leveraging advanced technologies, fostering innovation, and strengthening multi-stakeholder collaborations to build a resilient and sustainable digital ecosystem for all citizens.
Key future prospects include the continued rollout of advanced network technologies like 5G, which promises ultra-fast speeds and low latency, essential for supporting emerging applications such as IoT, AI, and smart city initiatives across urban centers. Moreover, ongoing efforts to optimize satellite and fiber optic networks will ensure robust backbones reach even the most remote islands, enhancing the reliability of last-mile connectivity. Government policies are increasingly focused on creating a conducive regulatory environment that attracts foreign investment, promotes local innovation, and develops a digitally skilled workforce to fully harness the potential of these technological advancements.
(For an overview of Indonesia’s strategic vision for a future digital economy, inclusive urban transformation, and 5G development, refer to the Indonesia Digital for Future Economy and Inclusive Urban Transformation White Book).
This ambitious roadmap positions Indonesia to fully capitalize on the opportunities presented by the Fourth Industrial Revolution. By proactively addressing future connectivity needs and fostering an innovation-friendly environment, the nation can enhance its global competitiveness, diversify its economy beyond traditional sectors, and further improve public services through digitalization. Ultimately, these future prospects aim to create a truly connected society where every Indonesian, regardless of location, can participate in and benefit from the digital age, ensuring a prosperous and equitable future.
Video Insight: Indonesia’s 5G Roadmap & Digital Transformation
For an insight into Indonesia’s strategic direction regarding future connectivity, including the 5G roadmap, watch this video from Kominfo (Ministry of Communication and Informatics):
Titled ‘International Virtual Conference: Indonesia 5G Roadmap & Digital Transformation’, this video highlights the government’s plans and vision for leveraging next-generation cellular technology to drive digital transformation and achieve its long-term development goals.
Conclusion: Paving the Way for a Connected & Prosperous Indonesia
In conclusion, Indonesia’s future connectivity landscape is poised for significant advancements, driven by a clear vision for universal digital access and economic transformation. By strategically investing in advanced technologies like 5G, fostering innovation, and strengthening multi-sectoral collaborations, the nation aims to build a comprehensive digital ecosystem. This proactive approach is crucial not only for enhancing global competitiveness but also for ensuring that the benefits of the digital age are inclusively shared, ultimately leading to a more connected, prosperous, and resilient Indonesia.
Conclusion: Indonesia’s Digital Destiny – A Connected and Empowered Archipelago
Indonesia’s ambitious journey towards a fully connected digital society is a testament to its resolve in overcoming unparalleled geographical complexities. Through landmark initiatives like the Palapa Ring fiber optic network, which forms the nation’s digital backbone, and the strategic deployment of advanced satellite technologies such as SATRIA-1 to bridge the ‘last mile’, the archipelago has made monumental strides in extending high-speed internet access to its vast and diverse population. These foundational efforts have not only laid critical infrastructure but have also served as a powerful catalyst for transformative change across vital sectors.
The pervasive digital connectivity is profoundly reshaping Indonesia’s landscape, fueling the digital economy. This includes democratizing access to education through digital learning, enhancing healthcare delivery via telemedicine, and notably empowering millions through inclusive digital and financial innovation, as well as showcasing how e-commerce is transforming MSMEs, especially in remote regions. While significant challenges persist, particularly in addressing the digital divide, Indonesia’s proactive vision for universal digital access, including the adoption of 5G and smart city initiatives, underscores its commitment to an inclusive and resilient digital future.
By continuously investing in innovation, fostering public-private partnerships, and nurturing digital literacy, Indonesia is set to harness the full potential of the digital age.
Ultimately, Indonesia’s connectivity revolution is more than a technological achievement; it is a national endeavor to ensure that every citizen, regardless of their location across the sprawling archipelago, can participate in and benefit from the opportunities of the modern digital world, forging a more equitable, prosperous, and globally competitive nation.
Frequently Asked Questions about Indonesia’s Connectivity Projects
What is Indonesia’s Palapa Ring network?
The Palapa Ring is Indonesia’s national fiber optic backbone network that spans over 36,000 km. It connects 514 cities and regencies across the archipelago, forming the core infrastructure for high-speed internet distribution.
What is the SATRIA-1 VHTS satellite?
SATRIA-1 is Indonesia’s first Very High Throughput Satellite (VHTS), launched in 2023. It delivers up to 150 Gbps capacity to remote and underserved areas, complementing the Palapa Ring by covering locations where fiber optic connections are not feasible.
How do the Palapa Ring and satellite internet work together?
The Palapa Ring serves as a high-capacity fiber optic backbone, while SATRIA-1 provides last-mile internet access to isolated regions. This hybrid model combines the reliability of fiber with the reach of satellite technology for nationwide coverage.
What is Indonesia’s biggest last mile connectivity challenge?
The main challenge is building local backhaul and distribution networks to deliver the Palapa Ring’s capacity to end-users. Without adequate last mile infrastructure, many remote communities remain unconnected despite the backbone’s presence.
How does Indonesia plan to improve rural internet infrastructure?
Indonesia plans to expand its satellite fleet with projects like SATRIA-2 and integrate advanced technologies such as 5G. This approach aims to strengthen rural connectivity, close the digital divide, and build a more inclusive digital ecosystem.
Trusted References
- Asvial, N. (2019). National fiber optic backbone strategies in rural areas of Indonesia. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIRD47319.2019.9074750
- Eschachasthi, E., Purwa, H. J., & Cendekia, S. (2022). Positive and significant impact of PRP infrastructure on connectivity, though not necessarily on direct economic activity. https://doi.org/10.34123/icdsos.v2021i1.99
- Lestariningsih, E. (2024). The Impact of Digital Divide on Indonesian Public Services: Low Digital Literacy and Inequality in Access. Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan Indonesia, 4(1), 77-85. https://doi.org/10.29210/020244613
- Putra, R. M., et al. (2024). Techno-economic analysis of SATRIA-1’s role in government communications. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMNETSAT63286.2024.10862510
- Tim Penulis. (2023). *Digital technology development on Indonesia’s economic growth*. International Journal of Research and Review. https://www.ijrrjournal.com/IJRR_Vol.10_Issue.9_Sep2023/IJRR32.pdf
- Tim Penulis. (2024). *Effectiveness of online learning platforms in increasing educational access in remote areas*. Proceeding of International Seminar On Student Research In Education, Science, and Technology. https://journal.ummat.ac.id/index.php/issrectec/article/view/22422
- Tim Penulis. (2024). *Teleconsultation readiness and disparities in Indonesian healthcare facilities*. Frontiers in Public Health. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11382234/
- Kementerian Koordinator Bidang Perekonomian. (Tanggal tidak diketahui). *Indonesia Digital for Future Economy and Inclusive Urban Transformation White Book*. https://ekon.go.id/source/publikasi/white-book-indonesia-digital.pdf
